Updated on March 12, 2023
The choice between induction and electric cooktops is a common one, whether you’re shopping for a new range or looking for range alternatives for a new home. Both have the power, precision, and performance to give quick heat and excellent heat control. You can make a better choice for your kitchen if you understand the differences between an induction and an electric cooktop.
Which Is Better Electric or Induction Cooktop
If you’re debating between an induction and an electric cooktop, the decision is entirely up to you. It all comes down to what you want and what is most important to you. Electric cooktops are the best option if you like to stick with what you know. An induction cooktop is the perfect choice if you want a cooktop that heats evenly and quickly, saves you money on electricity, and increases your safety by preventing heat transfer.

On the other hand, if you’re concerned about your carbon footprint, an induction cooktop might be a better option. It’s preferable to go with an electric cooktop instead of a gas one if you’re on a budget and don’t need a certain set of pans. As always, your cooking style, kitchen requirements, and money will all play a role in your final pick.
Is an Electric Stove Top Safe
Electric stoves are generally safe, but operator error and appliance failures can lead to dangerous situations. These may be avoided with good care and maintenance, allowing you to get the most out of your stove.
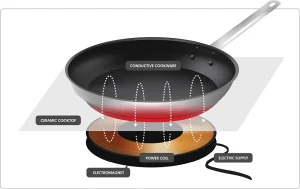
How Do Induction Cooktops Work?
Because they don’t use gas to generate heat, induction cooktops might be considered electric. Induction cooktops, on the other hand, use coils beneath the surface to generate heat. An induction stove uses the majority of its electricity to heat meals. Instant heat and temperature control are provided because there is no energy escaping.
Radiation from electromagnetic waves travels via the induction ring and into the cookware, where an electrical current alternates. As a result, the pot or pan begins to heat, and your food begins to cook in it. Because the air between the cooktop and pan never gets hot, there is no residual heat with an induction cooktop.
Pros
- Installing and using it is a breeze.
- Allow for a small amount of lingering heat to keep food warm or simmer
- Controlled and monitored heating might help you save money on your energy bill.
Cons
- Even in homes without children, residual heat can be hazardous.
- Heat-up time for electric cooktops is significantly longer.
- Coils are notorious for distributing heat in an unbalanced manner.
How Do Electric Cooktops Work?
Electric cooktops, also referred to as radiant cooktops, generate heat from a central location. A metal coil beneath the glass or ceramic surface of an electric cooktop conducts an electrical current. The electrical resistance causes the coil to heat up and light. Through the glass, infrared energy will be used to transport its heat. It’s important to note that only the burner on which you have your pot or pan will be heated. The transfer of heat from the cooktop to the pot then cooks your meal.
An indication light is common on electric cooktops since the burners retain heat for an indeterminate amount of time after they’ve been turned off.
Pros
- After cooking, cooktops are still chilly to the touch.
- Because the surface is still cool, it is easier to clean.
- Because there is no residual heat, energy expenses are reduced and the kitchen is kept cooler.
- Boiling water in half the time on gas means quicker meals.
Cons
- Usually more expensive than electric equivalents
- This method necessitates the use of induction-compatible cookware, such as iron or stainless steel pans.
- An buzzing sound may be heard at higher levels.
- A digital thermometer can be affected by a magnetic field.
What’s the difference between an induction and electric cooktop?
Glass-ceramic cooktops are now commonplace, and the components are located beneath the surface. Your meal will be warmed by these so-called radiant elements, which heat the cooking zone and radiate heat to the cooking utensils, so warming your food. A few minutes of preheating time is required before adding your meal whether searing steak or making an omelette, both of which have a quick cooking time.
Electric cooktops feature a smooth top, while induction cooktops have coiled copper wires beneath the flat surface. A magnetic current is created when an electric current flows through these metal coils, which heats pots and pans without heating the cooktop itself.
Induction cooktops heat up pots and pans significantly more quickly than gas or electric cooktops due to this direct heat transfer. Because of this, you won’t have to wait for a skillet to heat up before you begin browning your pork chops or melting your butter. Boiling water for a large batch of pasta takes no more than 15 minutes.
Induction cooktops are more sensitive than electric cooktops because induction elements respond immediately when you turn them on and off. An induction cooktop gives you complete control over the temperature. It’s best to lower the heat setting as soon as your soup reaches a boil so that it doesn’t boil over or spatter.
Heating devices that use induction technology are also quite accurate. Once you’ve chosen a temperature, it won’t fluctuate. As long as you’re simmering something like marinara sauce or a pot roast, you don’t have to worry about constantly stirring or adjusting the heat. In order to avoid gritty chocolate or brown butter when melting chocolate and butter for brownies, keep the heat at a low setting.
Induction cooktops are also safer than electric cooktops because they don’t use electricity.
You don’t have to worry about getting burned if you accidentally turn on an induction device without a pot on top of it. Induction cooktops are also much quieter than electric ones, even while they’re in use. Despite the fact that the cooktop’s surface does not heat up, it can absorb heat from a hot pan.
Using an induction cooktop is also safer than using a gas cooktop, which has an open flame. Accidental leaks of gas or carbon monoxide are also eliminated.
Five to 10% less energy is used by induction cooktops, and they are three times more efficient than gas cooktops. This is due to the fact that no heat is lost to the air and is instead transmitted directly to the cookware. It will save you money on both your cooking and heating bills. Even if the savings for your family are modest, the greater the national savings from induction cooktops, the better it is for the environment in the long run.
Is my induction cooktop compatible with my current pots and pans?
It all depends. Cookware must be magnetic in order to work with induction. On an induction cooktop, any pot or pan that has a magnet on the bottom will operate. Stainless steel, cast iron, and enamelled cast iron are all covered.
As a side note, it is possible to use magnetic pots and pans, but unless the bottom is absolutely level, they will not disperse heat evenly. Place a ruler over the bottom of your cookware once it has been turned upside down. The pan will heat evenly if the edge of the pan contacts the entire surface. It’s best to use pans with a flat bottom disc connected.
Do induction cooktops use radiation?
Induction cooktops emit electromagnetic radiation that is non-ionizing or low-frequency. The health effects of this sort of radiation are unknown.
Are induction cooktops noisy?
Induction burners may hum, buzz, or click for some people. Cookware that is too light or bent to completely cover the burner may be the blame for the noises. Avoid this problem by using hefty, well-made pans that match the burner size. Initially, the noise can be a little unnerving, but it’s not loud enough to interrupt conversation.

